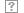"Lord Jesus, it is for thee that I patiently endure this cruel death. I pray thee to have mercy on my enemies."
Early in his monastic career, Martin Luther, rummaging through the stacks of a library, happened upon a volume of sermons by John Huss, the Bohemian who had been condemned as a heretic. "I was overwhelmed with astonishment," Luther later wrote. "I could not understand for what cause they had burnt so great a man, who explained the Scriptures with so much gravity and skill."
Timeline |
|
|
1321 |
Dante completes Divine Comedy |
|
1348 |
Black Death hits Avignon |
|
1349 |
Death of William of Ockham |
|
1369 |
John Huss born |
|
1415 |
John Huss dies |
|
1431 |
Joan of Arc burned at stake |
Huss would become a hero to Luther and many other Reformers, for Huss preached key Reformation themes (like hostility to indulgences) a century before Luther drew up his 95 Theses. But the Reformers also looked to Huss's life, in particular, his steadfast commitment in the face of the church's cunning brutality.
From foolishness to faith
Huss was born to peasant parents in "Goosetown," that is, Husinec, in the south of today's Czech Republic. (In his twenties, he shortened his name to Huss—"goose," and he and his friends delighted in making puns on his name; it was a tradition that continued, especially with Luther, who reminded his followers of the "goose" who had been "cooked" for defying the pope).
To escape poverty, Huss trained for the priesthood: "I had thought to become a priest quickly in order to secure a good livelihood and dress and to be held in esteem by men." He earned a bachelor's, master's, and then finally a doctorate. Along the way he was ordained (in 1401) and became the preacher at Prague's Bethlehem Chapel (which held 3,000), the most popular church in one of the largest of Europe's cities, a center of reform in Bohemia (for example, sermons were preached in Czech, not Latin).
During these years, Huss underwent a change. Though he spent some time with what he called a "foolish sect," he finally discovered the Bible: "When the Lord gave me knowledge of Scriptures, I discharged that kind of stupidity from my foolish mind."
The writings of John Wycliffe had stirred his interest in the Bible, and these same writings were causing a stir in Bohemia (technically the northeastern portion of today's Czech Republic, but a general term for the area where the Czech language and culture prevailed). The University of Prague was already split between Czechs and Germans, and Wycliffe's teachings only divided them more. Early debates hinged on fine points of philosophy (the Czechs, with Wycliffe, were realists; the Germans nominalists). But the Czechs, with Huss, also warmed up to Wycliffe's reforming ideas; though they had no intention of altering traditional doctrines, they wanted to place more emphasis on the Bible, expand the authority of church councils (and lessen that of the pope), and promote the moral reform of clergy. Thus Huss began increasingly to trust the Scriptures, "desiring to hold, believe, and assert whatever is contained in them as long as I have breath in me."
A political struggle ensued, with the Germans labeling Wycliffe and his followers heretics. With the support of the king of Bohemia, the Czechs gained the upper hand, and the Germans were forced to flee to other universities.
The situation was complicated by European politics, which watched as two popes vied to rule all of Christendom. A church council was called at Pisa in 1409 to settle the matter. It deposed both popes and elected Alexander V as the legitimate pontiff (though the other popes, repudiating this election, continued to rule their factions). Alexander was soon "persuaded"—that is, bribed—to side with Bohemian church authorities against Huss, who continued to criticize them. Huss was forbidden to preach and excommunicated, but only on paper: with local Bohemians backing him, Huss continued to preach and minister at Bethlehem Chapel.
When Alexander V's successor, the antipope John XXIII (not to be confused with the modern pope by the same name), authorized the selling of indulgences to raise funds for his crusade against one of his rivals, Huss was scandalized and further radicalized. The pope was acting in mere self-interest, and Huss could no longer justify the pope's moral authority. He leaned even more heavily on the Bible, which he proclaimed the final authority for the church. Huss further argued that the Czech people were being exploited by the pope's indulgences, which was a not-so-veiled attack on the Bohemian king, who earned a cut of the indulgence proceeds.
Scripture rebel
With that Huss lost the support of his king. His excommunication, which had been tacitly dropped, was now revived, and an interdict was put upon the city of Prague: no citizen could receive Communion or be buried on church grounds as long as Huss continued his ministry. To spare the city, Huss withdrew to the countryside toward the end of 1412. He spent the next two years in feverish literary activity, composing a number of treatises. The most important was The Church, which he sent to Prague to be read publicly. In it he argued that Christ alone is head of the church, that a pope "through ignorance and love of money" can make many mistakes, and that to rebel against an erring pope is to obey Christ.
In November 1414, the Council of Constance assembled, and Huss was urged by Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund to come and give an account of his doctrine. Because he was promised safe conduct, and because of the importance of the council (which promised significant church reforms), Huss went. When he arrived, however, he was immediately arrested, and he remained imprisoned for months. Instead of a hearing, Huss was eventually hauled before authorities in chains and asked merely to recant his views.
When he saw he wasn't to be given a forum for explaining his ideas, let alone a fair hearing, he finally said, "I appeal to Jesus Christ, the only judge who is almighty and completely just. In his hands I plead my cause, not on the basis of false witnesses and erring councils, but on truth and justice." He was taken to his cell, where many pleaded with him to recant. On July 6, 1415, he was taken to the cathedral, dressed in his priestly garments, then stripped of them one by one. He refused one last chance to recant at the stake, where he prayed, "Lord Jesus, it is for thee that I patiently endure this cruel death. I pray thee to have mercy on my enemies." He was heard reciting the Psalms as the flames engulfed him.
His executioners scooped up his ashes and tossed them into a lake so that nothing would remain of the "heretic," but some Czechs collected bits of soil from the ground where Huss had died and took them back to Bohemia as a memorial.
Bohemians were furious with the execution and repudiated the council; over the next several years, a coalition of Hussites, radical Taborites, and others refused to submit to the authority of the Holy Roman emperor or the church and fended off three military assaults. Bohemia eventually reconciled with the rest of western Christendom—though on its own terms (for example, it was one of the few Catholic regions that offered Communion of both bread and wine; the rest of Christendom simply received the bread). Those who repudiated this last compromise formed the Unitas Fratrum ("Union of Brethren"), which became the foundation for the Moravian Brethren (Moravia is a region in the Czech Republic), who would play an influential role in the conversion of the Wesley brothers, among others.

Support Our Work
Subscribe to CT for less than $4.25/month