Millennials used to be the group that churches and ministries were angling to evangelize. Now, all grown up and poised to overtake Baby Boomers as the largest generation, they’re the ones doing the evangelizing.
At least they should be.
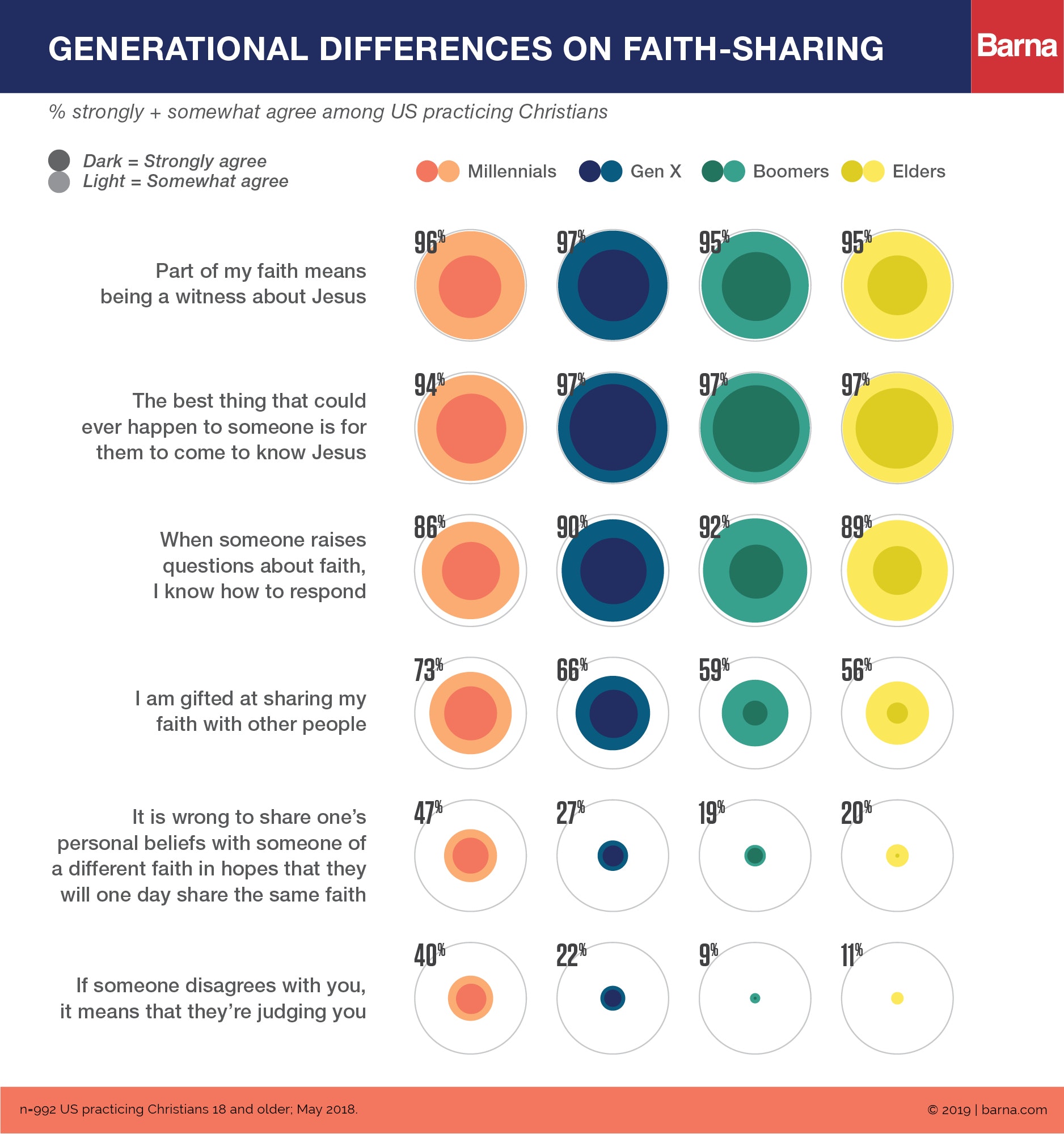
But new research from Barna Group and the creators of the Alpha course offers some disappointing news regarding the 20-somethings and 30-somethings now on deck to carry on the faith: nearly half (47%) of practicing Christian millennials—churchgoers who consider religion an important part of their lives—believe that evangelism is wrong.
They’re more than twice as likely as their parents and grandparents—Boomers and Elders, respectively—to say that it’s “wrong to share one’s personal beliefs with someone of a different faith in hopes that they will one day share the same faith.”
While this statistic could easily bolster stereotypes of a lazy, distracted, and increasingly unaffiliated generation, the minority of millennials who have stayed active in their churches also show higher markers of commitment in other areas, as well as a savvier sense of the religious pluralism and diversity they were raised around.
The recent Barna release found that, despite the reticence around the practice, millennials consider themselves good evangelists and still see themselves as representatives for their faith.
Nearly all practicing Christian millennials (96%) said witnessing for Jesus is part of being a Christian, and they were more likely than any other generation to say they were gifted at sharing their faith (73%).

And Barna previously found that millennials who identify as born-again were the most likely age group to share their faith—and that their evangelism habits were growing while other generations’ were dropping. In 2013, two-thirds of millennials said they had presented the gospel to someone within the past year, compared to half of born-again Christians in general.
Additionally, practicing Christian millennials have the strongest beliefs in the Bible and read it more than any other generation: 87 percent do so multiple times a week, according to a 2016 Barna survey on behalf of the American Bible Society (ABS).
So what’s behind their beliefs that evangelism is “wrong”?
Barna president David Kinnaman points to the rising cultural expectation against judging personal choices. Practicing Christian millennials were twice as likely as Gen X and four times as likely as Boomers and Elders to agree with the statement, “If someone disagrees with you, it means they’re judging you.”
“Cultivating deep, steady, resilient Christian conviction is difficult in a world of ‘you do you’ and ‘don’t criticize anyone’s life choices’ and emotivism, the feelings-first priority that our culture makes a way of life,” Kinnaman said. “As much as ever, evangelism isn’t just about saving the unsaved, but reminding ourselves that this stuff matters, that the Bible is trustworthy, and that Jesus changes everything.”
Several evangelicals’ reactions to the Barna release pointed to the need for better Christian formation for younger churchgoers.
“I’m a Millennial, and this is pure evidence of the failure of the church to prepare youths to understand faith/speak out,” tweeted author Billy Hallowell. “Beyond that, it’s also a result of the cultural crisis of secularism bombarding us at every turn.”
“You can’t pin the belief that evangelism is wrong on Facebook, distraction, disenchantment, or recession,” wrote Samuel James, a writer at First Things, on Twitter. “The data here strongly suggests that Christian millennials are being catechized by their colleges, not churches.”
In her book Reciprocal Church, Sharon Galgay Ketcham, a practical theologian at Gordon College, challenged Christian elders to give younger generations a chance to actively engage their faith in the church context rather than receive the traditions “passed on” to them. Two-thirds of churchgoing Christians will stop attending at some point in the years after turning 18—some returning regularly, some occasionally, and some not at all.
The rise of the religiously unaffiliated “nones,” now roughly a quarter of the population, has taken away the expectation for younger generations to identify as Christian just for the sake of it. Without the pull of “cultural Christianity,” leaders see the millennials who do stay involved in their churches as particularly committed and faithful.
“Though the Christian population of this generation is likely no higher than 15 percent, these young people may well turn the world upside down with their commitments and causes,” wrote LifeWay Christian Resources CEO Thom S. Rainer and son Jess R. Rainer in their book, The Millennials. “Millennial Christians are not content with business-as-usual churches. To the contrary, they will connect with churches on if those churches are wiling to sell out for the sake of the gospel.”
Millennial leaders have begun assuming the mantle at major churches and ministries. More than two dozen millennials now hold senior pastor positions at congregations with more than 1,000 attendees, with some megachurch pastors as young as 32, according to Leadership Network.
But evangelism remains a sticking point among a 21st-century crowd which sees tent revivals and tracts as a thing of the past. “Evangelism is often presented as an old school, out-of-style idea with little value or relevance in our fast-paced, urban world,” wrote Hannah Gronowski, the founder and director of Generation Distinct, for The Exchange last year.
Younger folks are tempted to believe instead, “if we just live good enough lives, we can forgo the conversation entirely, and people around us will almost magically come to know Jesus through our good actions and selfless character,” she said. “This style of evangelism is becoming more and more prevalent in a culture constantly looking for the fast track and simple fix.”