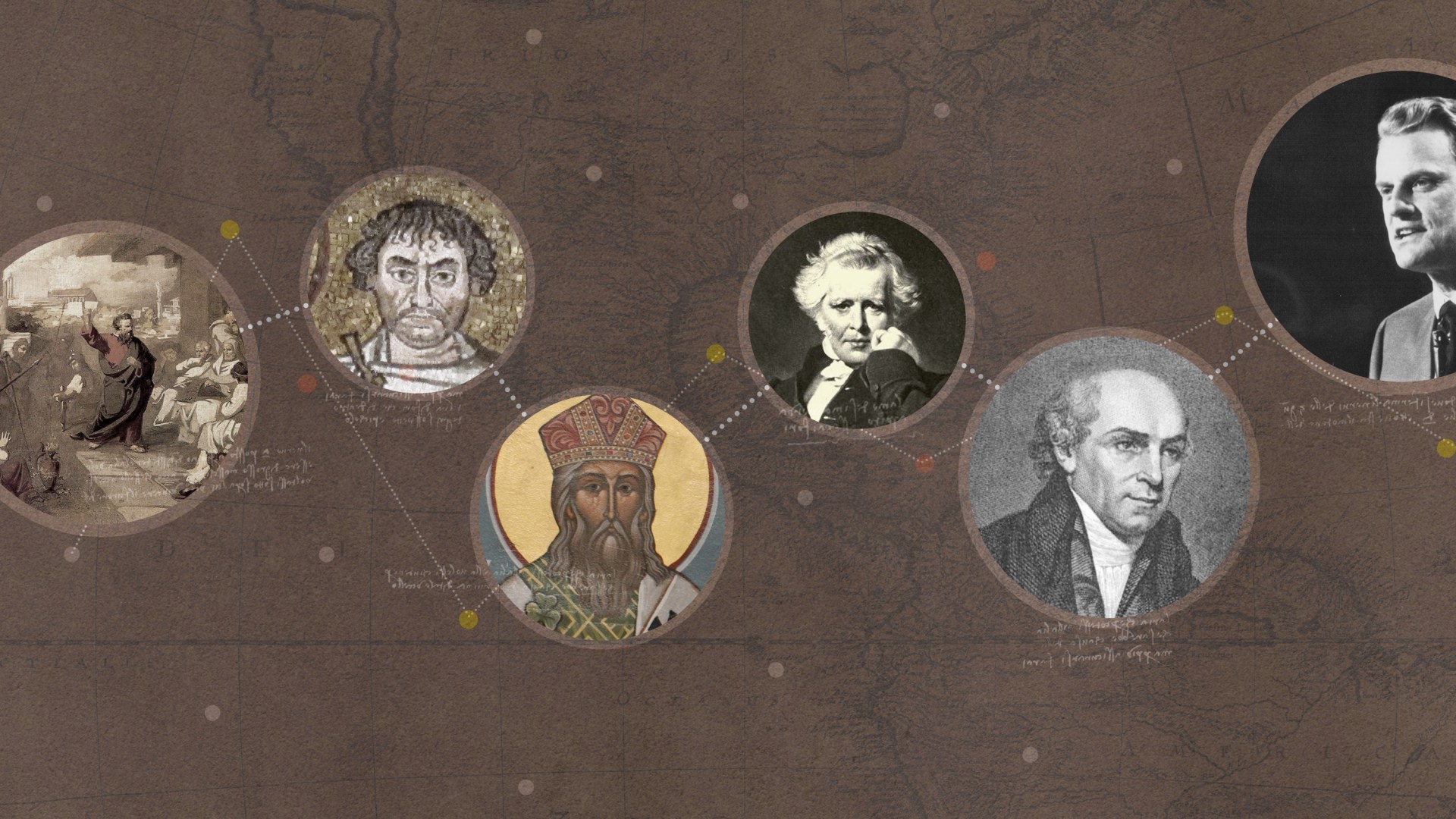
When Jesus delivered the Great Commission to a small band of disciples, they might have wondered how they were supposed to carry his gospel to the ends of the earth. Yet across the nations it spread, winning converts and planting churches everywhere it went. Alice T. Ott, a missions and world Christianity professor at Trinity Evangelical Divinity School, surveys the pivotal moments of this journey in Turning Points in the Expansion of Christianity: From Pentecost to the Present. Jay Riley Case, a historian of missions at Malone University, spoke with Ott about the big picture and the smaller details of Christianity’s global advance.
What got you interested in the history of the expansion of Christianity?
My interest is an outgrowth of my own experiences. I have loved history ever since I was a teenager. I spent 21 years of my adult life as a missionary in Germany. After my husband and I returned to the United States, I earned my PhD and started teaching courses on the history of mission and Christianity in the non-Western world. The book grew out of my research for these courses, as well as from my teaching and interacting with students.
The expansion of Christianity is an incredible story, but a challenging one to tell. Why did you choose “turning points” as the framework?
My inspiration came from Mark Noll’s book, Turning Points: Decisive Moments in the History of Christianity. I became convinced that a similar approach would be a great way to simplify the broad and complex history of Christian expansion. Rather than attempting to include every aspect of Christian expansion, I home in on crucial events and trends—on pivotal, decisive moments when something monumental changes.
Your book identifies many recurring themes in the history of Christian expansion. Can you name a couple that seem particularly significant for Christians today?
In the conclusion, I talk about five different themes that show up time and again in the history of Christian expansion. One is the theme of mission theology. I believe that theology profoundly influences mission practice. In other words, theology was often a major factor determining whether or not the various branches of the church were actively engaged in mission at particular times and in particular places. At various times during the history of the church, Christians embraced several theologies that actually dampened their motivation for mission. One of these—and this may surprise some people—was the belief that the Great Commission applied only to the original apostles, and not to all Christians in all ages.
Another theme that I discuss concerns mission agents and structures. Throughout history, the expansion of Christianity was not just a Western or even a missionary-driven enterprise. Rather, from the beginning the church has grown through the efforts of a variety of mission agents: Western and non-Western missionaries, as well as the witness of indigenous lay Christians.
The gospel spreads more quickly cross-culturally when there are good, appropriate structures for mission. In late antiquity and the Middle Ages, the monastic movement and later religious orders provided the mission organization, structure, and personnel for the Roman Catholic Church. Protestants initially lacked a similar organizational structure for mission. Only as they adapted their already-existing voluntary religious societies to the specific needs of mission did the Protestant mission movement take off.
The 1974 Lausanne Conference may be the turning point that resonates most with readers—perhaps because it is the most recent. What do you find most significant about it?
A key goal of Billy Graham and the steering committee of the Lausanne Conference was reaffirming an evangelical foundation for mission. But another important aspect is that Lausanne ’74 reflected evangelicalism’s increasingly multicultural, global identity. While evangelicalism today is sometimes barely holding its own in the West, it is exploding in many parts of Africa, Latin America, and Asia. And missionaries are flowing to and from every continent.
Lausanne ’74 also inspired and furthered the growth of mission movements in many important non-Western countries. In the book, I focus on Nigeria, South Korea, and Brazil, all of which have large numbers of cross-cultural missionaries today. Brazil, for example, has more foreign missionaries than any country except the United States.
Your book also highlights historical developments that may be quite foggy in our minds, if we even recall them at all. I, for instance, knew next to nothing about the East Syrian mission to China, and Henry Venn is not exactly a household name. Why should Christians know about these obscure incidents and people?
The East Syrian mission to China was actually the culmination of an early and centuries-long eastward expansion of Christianity. Remembering this eastward expansion helps us counteract the false impression that Christianity, from the beginning, was a largely Western or European phenomenon. Indeed, the first millennium saw vibrant churches in North Africa, Syria, Persia, Afghanistan, Central Asia, China, India—places where today the gospel is less widely known.
As for Henry Venn, he lived and served in the middle decades of the 19th century, about two generations into the Protestant mission movement. Venn was one of the earliest and most influential mission strategists. He developed theoretical and practical mission principles to achieve the ultimate goal of mission—a culturally appropriate, indigenous, independent, national church on the mission field. His “three-self” principles declared that an independent, indigenous church on the mission field needed to be self-supporting, self-governing, and self-propagating. That was a groundbreaking insight then, and it has ongoing relevance today.
What surprises or new insights did you encounter as you worked on this book?
As an evangelical, I was surprised and delighted to read the original writings of two fifth-century saints: Patrick of Ireland and Narsai of Persia, a representative of the East Syrian Church. Patrick’s Confession and Narsai’s sermons had elaborately developed and biblically based mission theologies, which many Christians would fully embrace today.
Another pleasant surprise was discovering that a common perception we have today—that missionaries from previous eras lacked cultural sensitivity—was not always true. Here are two examples. The 16th-century Jesuit missionaries in China and Japan attempted to accommodate the Christian message to the local religious cultures in quite an advanced and remarkable way. On the Protestant side, William Carey and the Baptist mission in Serampore, India, had surprisingly progressive views on the task of mission and on empowering the locals to evangelize. The Serampore Baptist missionaries covenanted with one another to study the Hindu culture well so that they would not be “barbarians” to the local population.
Many of us take the cross-cultural expansion of Christianity over history for granted, as though it just unfolded naturally. What should we better understand about this process?
There were some periods in Christian history when the gospel seemed to spread naturally—for example, in the early church. But that is usually not the case. God can certainly choose to use untrained or poorly trained missionaries to bring people into his kingdom, especially if they are loving and earn the respect and trust of the local people. But generally speaking, the most effective missionaries have immersed themselves in the local culture and achieved a substantial level of linguistic and cultural competency. That’s an important lesson to heed as we attempt to engage the world for Christ.