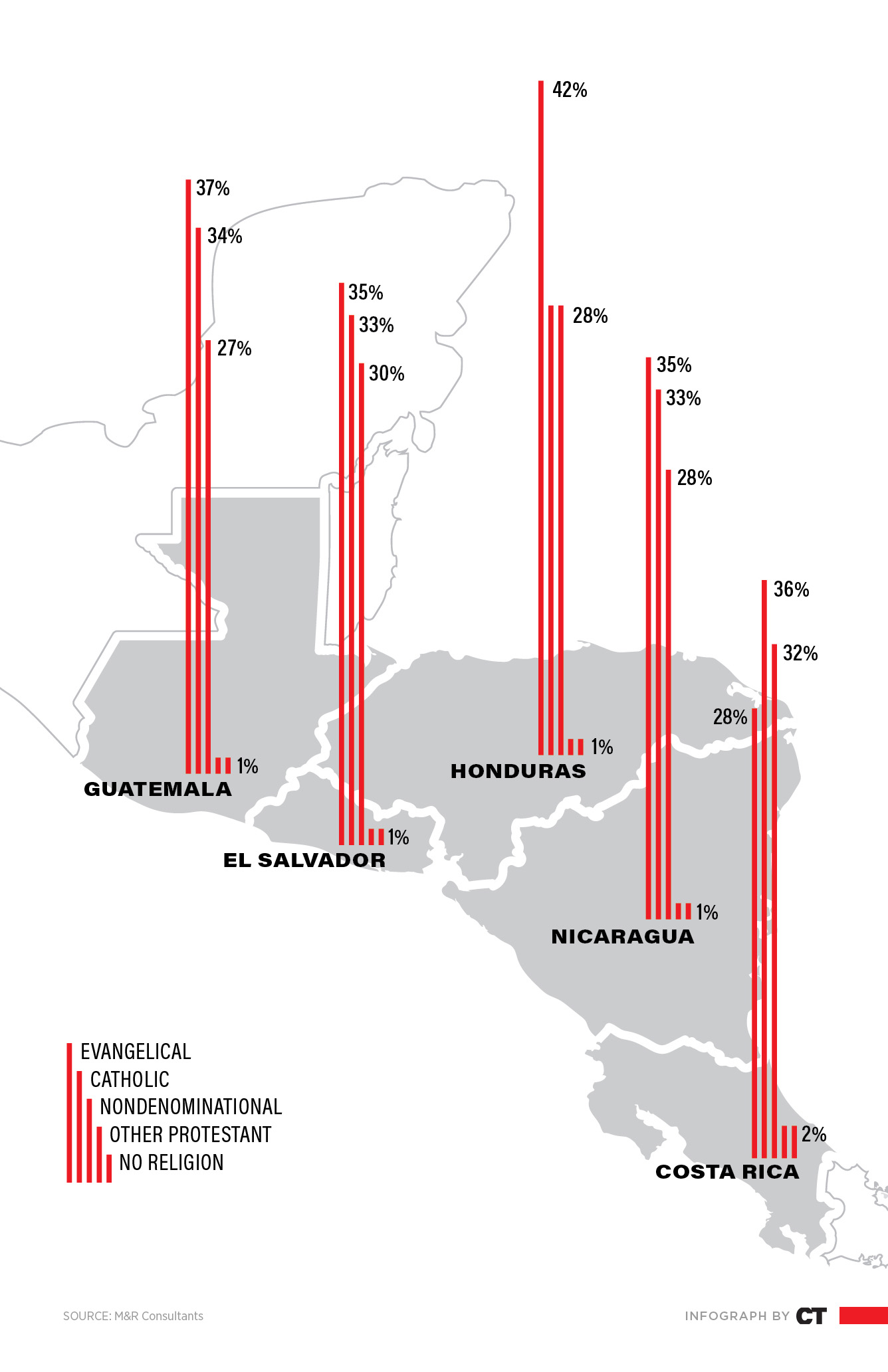
Evangelicalism is now the largest religious demographic in Central America, according to a poll of about 4,000 people in five countries. More than a third of people from Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica told researchers from M&R Consultants that they are evangelical, while another 29 percent said they are creyente sin denominación (nondenominational believers).
Only about a third of people in the region said they were Catholic—down from about 60 percent in the 1970s. Some scholars have attributed the shift to internal Catholic conflict and the long fallout from the church’s political affiliations on the extreme right and left, along with the disruptions of urbanization.
Evangelical theologian Samuel Escobar, noting the trend in an interview in 2006, said Catholics who moved to Central American cities found empowerment in their evangelical conversion. “Their decision to accept Christ meant a change in patterns of behavior which helped people to reorient their lives,” he said.
According to sociologist Ariel Goldstein, who is critical of evangelical involvement in the regions’ politics, evangelicals grow because they adapt to local customs, have clergy who live close to the people, innovate, use social media, meet practical needs, and create community.